Charge coupler (CCD) and charge Memory (Memory) as two independent branches in modern electronic system develop respectively along their own paths, carbon-based prototype devices with photoelectric sensing and storage functions have not been reported. The reporter learned from Shenyang National Research Center of Materials Science, Institute of Metals, Chinese Academy of Sciences, that the scientific researchers of the center cooperated with many domestic units and proposed a kind of carbon nanotube non-volatile memory based on aluminum crystalline floating gate, this provides a new device design method for wearable electronics and special environment detection systems.
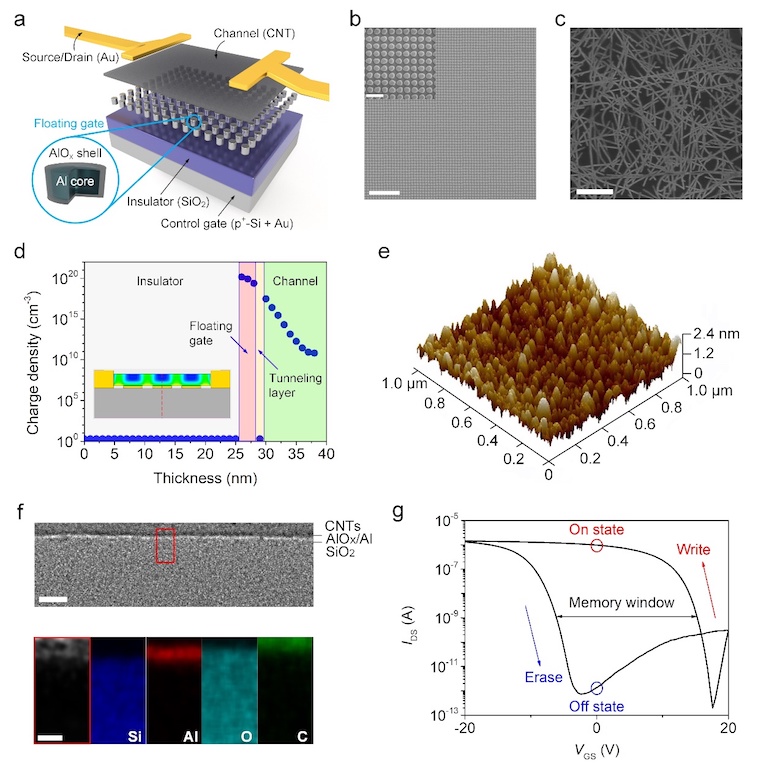
Picture Description: design and structure diagram of new devices. (Pictures provided by the interviewed company)
a) the schematic diagram of device structure; B) the lattice structure of aluminum/alumina nanocrystals with uniform and discrete distribution and c) the scanning electron microscope diagram of carbon nanotube film channel material; d) simulation of charge density distribution in the channel; e) surface topography map of aluminum nanoparticles; f) cross-section transmission electron microscope and element distribution map of carbon nanotube film and floating grid structure; g) storage window.
Recently, the achievement published a research paper entitled "flexible carbon nanotube sensing-memory device" on advanced materials. It is reported that the new type of device has high current-switch ratio, storage time as long as 10 years and stable read/write operation, and multiple separated aluminum nano floating grid devices have stable flexible service performance. More importantly, charges are generated by oxidation X the tunneling mechanism in the layer changes from Fowler-Nordheim tunneling to direct tunneling, thus realizing the sensing and detection of photoelectric signals; Based on theoretical calculation analysis and experimental optimization design, A non-volatile flexible ultraviolet light array device with 32 × 32 pixels has been prepared, which realizes the sensing and image storage of optical images for the first time and lays a foundation for the development of new flexible light detection and memory devices.
According to introduction, researchers use semiconductor carbon nanotube film as channel material, and use uniform and discrete distribution of aluminum and alumina integrated structure as floating grid layer and tunneling layer, high-performance flexible carbon nanotube floating gate memory is obtained, and the current switching ratio between read/write and erasure of the device is higher than 10 under 0.4% bending strain. 5, storage stability exceeds 10 8 seconds. At the same time, the extremely thin alumina tunneling layer can make the carrier "imprisoned" in the aluminum nanocrystal floating grid in erasure state obtain the light energy higher than the function of aluminum work, return to the channel through direct tunneling to significantly improve the closed current and complete the direct conversion and transmission of photoelectric signals, realize a new multifunctional photoelectric sensing and storage system integrating image sensing and information storage.
The research was jointly completed by researchers from metal Institute of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou Nano Institute of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Jilin University, and obtained the National Natural Science Foundation, metal Institute of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Academy of Sciences, supported by projects such as Shenyang National Research Center for Materials Science.


